BMI is calculated by using following formula:
BMI = Weight (in kilograms)
Height (m) X Height (m)
| BMI range - kg/m2 | Category |
| <18.5 | Underweight |
| 18.5-23.5 | Normal |
| 23.5-27.5 | Overweight |
| 27.5-37.5 | Obese |
| > 37.5 | Morbidly Obese |
| > 50 | Super Obese |
| > 60 | Super Super Obese |
Morbid obesity is a state of severe obesity defined by following BMI criteria.
Those who are morbidly obese are at greater risk for illnesses including diabetes, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), gallstones, osteoarthritis, heart disease, infertility and cancer.
If BMI > 23.5 then lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise is the appropriate choice of treatment. Increased physical activity or exercise, reducing calories and practicing healthier eating habits are vital to overcoming obesity.
: If BMI > 27.5 with co-morbidities or > 30 with or without co-morbidities, pharmacotherapy with weight loss drugs is the treatment option available. Close medical monitoring is required while taking a prescription weight-loss medication.
: If BMI > 32.5 with co-morbidities or > 37.5 with or without co-morbidities, Bariatric surgery is the appropriate choice of treatment. Weight-loss surgery for obesity may be considered if other methods to lose weight haven't worked.
Indians are genetically susceptible to weight accumulation, especially around the waist. An obese individual is much more susceptible to diseases like diabetes, hypertension, osteoarthritis and obstructive sleep apnoea.
Studies have shown that:
In MALES, Compared with a healthy weight man, an obese man is 5 times more likely to develop type 2 diabetes.
In FEMALES, An obese woman, compared with a healthy weight woman, is almost 13 times more likely to develop type 2 diabetes.
The traditional approach to treat TYPE 2 DM has been step wise introduction of lifestyle changes with or without oral medications, saving the insulin therapy for last. Treatment should focus equally on remission of both diabetes and obesity and needs to be widely understood. In the light of the escalating global diabetes crisis, the need of the hour is to identify interventions that provide a long term metabolic outcome (obesity and associated diseases remission). There are several methods for treating obesity, such as lifestyle changes encompassing behaviour modification, physical activity, diet modification and medical management. It has been seen that the sustained weight loss is achieved by only 10% of the population.
Bariatric surgery (Obesity surgery) is the most effective long-term treatment for obesity with the greatest chances for amelioration and even resolution of obesity-associated diseases. In the given scenario of increasing morbidity and mortality due to Type II Diabetes Mellitus and obesity, bariatric surgeries emerged as a promising treatment. It provides exceptional sustained weight loss and remission of type II diabetes in addition to improvement in other co morbidities and quality of life.
BMI or Body Mass Index is a measure of calculating a person’s excess weight
It is calculated by the following formula:
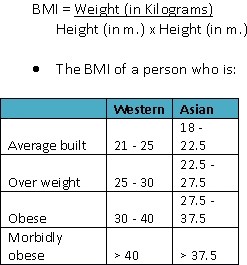 * We as Indians develop complications of obesity at lower BMI.
* We as Indians develop complications of obesity at lower BMI.